Which ones are better: horizontal or vertical solar panels? It is not a matter of preference or simple logic. Science has spoken, and scientists say go vertical.
It’s true that simple logic says horizontal panels are better. It would be:
- Firstly due to their orientation to the south, and
- Secondly, due to their leveled position towards the sky, they get the most sunlight.
To be precise, horizontal panels do not lay flat; they are angled to a certain degree depending on location. The angle is usually between 20-35 degrees. But that is determined by math formulas. Moreover, solar farms have systems to move panels following the sun’s orbit. Just, tracking systems cost a lot so they are not cost-effective for small solar farms.
The simple logic works so far so well. But what if the scientific facts show the opposite?
The Leipzig University of Applied Sciences researchers published a study in the last month’s edition of the journal Smart Energy. There they claim that bifacial solar panels mounted with one side facing east and the other facing west produce more renewable power. The reason is vertical panels mounted this way will reduce the abundance of electricity at midday and deficit in the mornings or afternoons. Uneven production of solar panel energy is one of the major flaws of traditional solar energy farms.
Vertical panels are more cost-effective
On the other side, the weakness of vertical solar panels is they are more expensive than horizontal solar systems. But, in a long term, they are more cost-effective. Here is why.
– Positioned east-west they have more hours of available solar power (So, no need for gas power plants for support.)
– They can be mounted on agricultural surfaces to be so-called APV (agri-photovoltaic) systems
-
- That’s an opportunity for extra profit for farmers
- It makes more available places for renewable vertical solar panels
- It protects crops from excessive wind and heat
- Countries with a high density of citizens in a small area, do not have to choose between food production or electricity production
– Compared to standard horizontal solar panel farms, there is a decrease in battery storage needs
– Vertical solar panel plant saves 1 megaton of CO2 per year on every 40 gigawatts produced solar energy
– Vertical solar panels have more even energy production; they skip production peaks at midday like horizontal panel farms (This is usually waste energy if not stored properly. But, the storage costs.)
– Most electricity generation is in the mornings and evenings when is most needed
Comparing vertical solar panels’ performance
The Leipzig University of Applied Sciences chart below shows typical solar power production with a conventional orientation, an east-west orientation, a north-south orientation, and a combination of orientations.
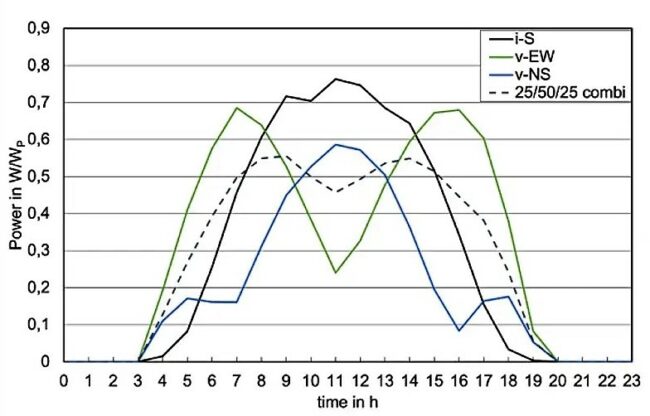
The numbers speak for themselves. Compared to the conventional horizontal solar farm, east-west oriented vertical solar panels farm begins electricity production hours earlier in the day and continues power production hours later in the day. And there is no midday solar energy over-production that exceeds the demand.
All in all…
To summarize, German researchers claim vertical solar panels may be better than horizontal solar panels. But, the combination of both is probably the best. Vertical solar panels can supply the utility grid with renewable energy when horizontal panels can’t. So we can skip thermal or nuclear generating plants for power to cook our dinner.

